Support for profiles and proxy settings
Problem
In enterprise networks, it is relatively common to have not just firewall protection network traffic but also a network proxy to control the outgoing traffic.
This is a thing where you really should be in contact with your IT.
With the tooling guided here, you can get to the correct solution that you can distribute as a configuration file.
Leveraging your IT to use the tooling and set these things up will make the issue invisible to regular users.
Network proxies are a field of science on their own, and there are A LOT of different setups and ideologies around the topic.
Because of the variance in setups and methodologies, most command-line and developer tools cannot rely on the operating system to get all the settings needed. Most tools implement simple support and almost always depend on some tool-specific environment variables to get the details.
A proxy can be a simple one that can work just with a simple setup of HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY environment variables.
Conversely, a heavy-duty setup can involve restrictions that only allow access to outside networks from a specific network inside the company. Machines need the correct client certificates or passwords to access the proxy server and require a separate certificate to re-enable HTTPS traffic between the machine and the proxy server.
How to test if you are even affected by this
IT departments should resolve these things, so as an end-user or even a developer, you should NOT need to do these.
The simplest way to test things is to get RCC, create a template robot, and try to run that.
If the run is successful, you are done! If the execution fails, continue reading.
What
RCC Profile Configuration provides a way to create, test and distribute proxy configurations in a single format for all the tools involved. The profile configurations support many things on top of just the proxy settings, so the RCC documentation on the topic is worth a look-see.
Because the configuration is done and controlled by RCC, all Robocorp tools get these settings from a single source, so when you switch to a profile, all tools switch without the need to set things one by one.
With the profile configuration, you can control the following aspects:
- Proxy settings
- Certificate for proxy access
- Enable/disable SSL verifications
- Enable/disable SSL revocations
- Specify tool-specific config files for
pipandmicromamba - Set the Robocorp Control Room endpoints
- This is valid for enterprises that have separate SSO login
In general, the RCC profile config gives a lot of control for setting the behavior in enterprise settings.
How
Reminder that creating a profile is a one-time task for someone who knows the network setups.
👉 Running the tooling in the target network also enables immediate testing, which is highly recommended.
Always refer to the RCC Profile Configuration documentation for the latest commands.
- Start by getting and editing the default settings content:
rcc config settings > start.yaml- You can then edit most values into the
start.yaml-file you created.
- The next step is to run the interactive configuration setup, but before that, it is good to have these ready:
- Have your edited
start.yamlfile ready - If your proxy needs a client certificate, you need that exported in a PEM file.
- If you have a
pip.iniconfig file, have the file ready - If you have a mamba/conda config file, have the file ready
- Have your edited
- Now run:
rcc interactive config- RCC gives you an interactive sequence of questions to create a new profile using the details you give.
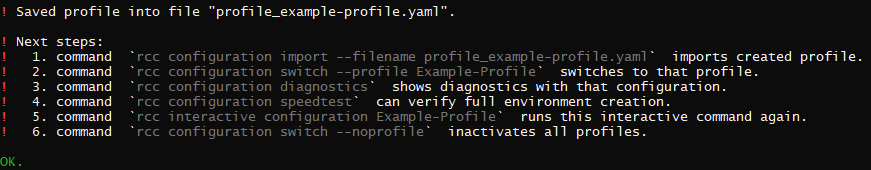
- You can now test the profile you just made according to the guide
RCCprovides:- Import the profile, switch to it, and run the diagnostics and speed test.
- If all pass, you have created a working profile.
- If something fails, you can repeat the interactive creation with different setups until you succeed.
- Once you have a tested configuration, you can deploy the configuration to others.
Deploying profiles
Once done, the profile is just a single YAML file with a filename pattern like: profile_example-profile.yaml.
- If you know the
ROBOCORP_HOMEpath on the users' machines, you only need to get the profile file to that folder.- By default the location is on Windows:
%localappdata%\robocorpand on Linux & macOS:~/.robocorp
- By default the location is on Windows:
- You can also use
RCCto import the profile to the correct location by running the command:rcc config import -f <your profile yaml filename>
- Users can have multiple profiles if needed
Using and switching profiles
- List the profiles:
rcc config switch- The output lists the name and description given when the profile was created.
- Use a profile:
rcc config switch -p <name of the profile>RCCextracts the profile settings and optional certificates into theROBOCORP_HOMEand can share the settings with Robocorp tools and applications.